
What is Redis?
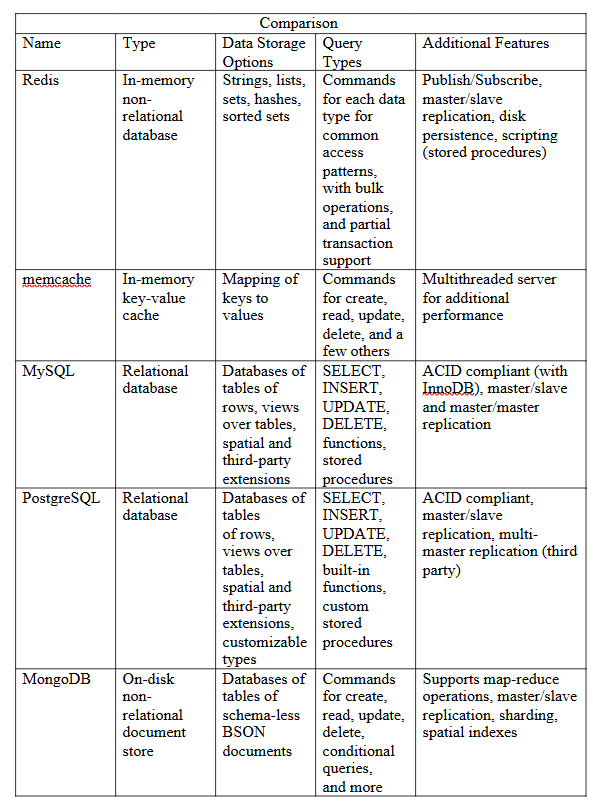
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store that may be used as a database, cache, or message broker. It supports several data structures including strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, hyper loglogs, and geospatial indexes. Redis is characterized by its performance, simplicity, and versatility.
Key Features of Redis
- In-Memory Data Store: Held in memory, with ultra-fast read and write operations.
- Persistence: Offers methods such as snapshotting and append-only file (AOF).
- Data Structures: Supports strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, and more.
- Pub/Sub Messaging: Allows for real-time messaging and notifications.
- High Availability: Implements Redis Sentinel for monitoring and fail-over.
- Cluster Support: Goes all the way towards data distribution across multiple nodes with Redis Cluster.
- Extensibility: Provides for modules of custom commands and functionality.
- Lua Scripting: Can execute Lua scripts natively on the server. Atomic Operations: Commands like increment, decrement, and list operations are atomic in nature.
- Replication: Provides for master-slave replication, thus making sure data is not lost in case of failure, which can easily scale to higher data.
Uses of Redis
- Caching: Stores frequently accessed data to decrease database load and latency.
- Session Management: User sessions in web applications can be managed.
- Real-time Analytics: It is capable of handling real-time data streams like user activity or stock prices tracking.
- Leaderboards: This helps to build a real-time ranking system by making use of sorted sets.
- Message Queues: This can act as a lightweight message broker.
- Geospatial Indexing: It stores and queries geospatial data in an efficient way.
- Pub/Sub Systems: One can use this to build a chat application, notification, or live feeds.
- Machine Learning: Serve pre-computed ML models and features.
- Gaming Applications: Manage game states, leaderboards, and matchmaking.
How to Implement Redis
1. Installation
- Linux: Use apt-get install redis or yum install redis.
- macOS: Install via Homebrew: brew install redis.
- Windows: Use WSL or download from third-party Redis for Windows projects.
2. Basic Commands
- Start Redis server: redis-server
- Connect using the CLI: redis-cli
- Common commands:
a) SET key value: Set a value.
b) GET key: Retrieve a value.
c) DEL key: Delete a key.
d) EXPIRE key seconds: Set expiration time.
e) INCR key: Increment value
3. Config
Modify the redis.conf configuration for parameters, such as Persistence: Persist to AOF by append only yes. Security: Add a password using the requirepass. Max Memory: Specify limitations with max memory and eviction strategies. Log: Configure levels and logfiles.
4. Client libraries Redis supports many client libraries in multiple languages such as Python (redis-py), Node.js (ioredis), Java (Jedis), and PHP (Predis or phpredis).
Redis in Laravel Framework
Redis is neatly supported in Laravel because Laravel supports Redis out of the box.
- Prerequisites
Install Redis on your system and ensure that Redis is running.
2. Installation of PHP Redis Extension
You can install the PHP Redis extension by using the following command: Linux/macOS: pecl install redis Windows: Copy the Redis DLL to the PHP extensions folder and uncomment it in php.ini.
3. Laravel Configuration
Add Redis to the config/database.php file:
'redis' => [
'client' => env('REDIS_CLIENT', 'phpredis'),
'default' => [
'host' => env('REDIS_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'password' => env('REDIS_PASSWORD', null),
'port' => env('REDIS_PORT', 6379),
'database' => env('REDIS_DB', 0),
],
'cache' => [
'host' => env('REDIS_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'password' => env('REDIS_PASSWORD', null),
'port' => env('REDIS_PORT', 6379),
'database' => env('REDIS_CACHE_DB', 1),
],
],
Update the .env file:
- REDIS_CLIENT=phpredis
- REDIS_HOST=127.0.0.1
- REDIS_PASSWORD=null
- REDIS_PORT=6379
- REDIS_DB=0
- REDIS_CACHE_DB=1
Usage in Laravel
Caching:
- Cache::store(‘redis’)->put(‘key’, ‘value’, 3600); // Store in cache
- Cache::store(‘redis’)->get(‘key’); // Retrieve from cache
- Session Storage: Update SESSION_DRIVER in.env to redis.
- Queues: Set QUEUE_CONNECTION to redis in.env.
- Broadcasting: Configure Redis as a broadcasting driver to implement real-time notifications.
Best Practices with Redis
- Monitor Usage: Use redis-cli or tools like RedisInsight.
- Set Expiration: Employ EXPIRE or TTL to stop uncontrolled growth.
- Utilize Namespaces: Use the keys with prefix to better arrange.
- Use Redis Cluster: Scale up to handle large-sized applications.
Secure Redis:
- Make use of secure passwords
- Redis bind only on specific IP.
- Activate TLS.
- Back up the server: Snapshotting or AOF should be turned on.
- Minimize abuse: Redis can only be utilized when data stored needs in-memory speeds.
- Code Efficiency: Implement Lua script codes for extensive computations.
- Optimized Eviction: Select an appropriate eviction policy for eviction such as volatile-lru, allkeys-lru etc.
Tools and Libraries
- RedisInsight- GUI management for Redis
- Predis: a PHP extension allowing interaction with Redis
- Redis Modules:
a) RedisJSON : Json support
b) RediSearch : Full text Search
c) RedisTimeSeries: manage time-series data
d) RedisBloom : Probabilistic Data Structures
e) Redis Sentinel- provide high availability for Redis applications automatically
f) RedisGraph: Redis’ graph database.
Connect with Redis client API libraries:
Use the Redis client libraries to connect to Redis servers from your own code. Following client libraries for six main languages:
Community-supported clients
The table below shows the recommended third-party client libraries for languages that Redis does not document directly:
redis-py guide (Python)
Connect your Python application to a Redis database
redis-py is the Python client for Redis. The sections below explain how to install redis-py and connect your application to a Redis database.
redis-py requires a running Redis or Redis Stack server. See Getting started for Redis installation instructions. You can also access Redis with an object-mapping client interface.
Install
To install redis-py, enter:
pip install redis
For faster performance, install Redis with hiredis support. This provides a compiled response parser, and for most cases requires zero code changes. By default, if hiredis >= 1.0 is available, redis-py attempts to use it for response parsing.
pip install redis[hiredis]
Connect and test
Connect to localhost on port 6379, set a value in Redis, and retrieve it. All responses are returned as bytes in Python. To receive decoded strings, set decode_responses=True. For more connection options, see these examples.
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, decode_responses=True)
Store and retrieve a simple string.
r.set('foo', 'bar')
# True
r.get('foo')
# bar
Store and retrieve a dict.
r.hset('user-session:123', mapping={
'name': 'John',
"surname": 'Smith',
"company": 'Redis',
"age": 29
})
# True
r.hgetall('user-session:123')
# {'surname': 'Smith', 'name': 'John', 'company': 'Redis', 'age': '29'}
Redis is a powerful and versatile tool for all kinds of use cases, from caching to real-time analytics. With its increasing feature set and community support, Redis remains a critical component of modern application architecture. Its flexibility and performance make it an essential technology for developers who want to build scalable, high-performance applications.
References:
https://dev.to/woovi/simple-cache-with-redis-5g3a
https://laravel.com/docs/11.x/redis
https://redis.io/docs/latest/develop/clients/
https://redis.io/ebook/part-1-getting-started/chapter-1-getting-to-kn…

