
What is 5G?

5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, succeeding 4G LTE. It is designed to deliver faster and more reliable communication networks, with significantly lower latency and higher capacity than its predecessors. By leveraging new technologies and spectrum, 5G aims to enable a wide range of innovative applications, from enhanced mobile broadband to massive machine-type communications and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.
Understanding 5G: What Sets it Apart?
At its core, 5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, offering significantly faster data speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity compared to its predecessors. While 4G LTE paved the way for mobile broadband, enabling services like video streaming and online gaming on-the-go, 5G takes connectivity to new heights.
Key Features of 5G:
What is 5G capable of?
Imagine living in a world where people, gadgets, buildings, and infrastructure talk to each other. In this world, doctors can conduct surgeries from thousands of miles away; cars drive on their own; buildings, factories and cities can interact with you; and you can shop and watch live sports events in VR!
Now open your eyes, because we’re not talking about a sci-fi movie here. Rather, this is what our world will become thanks to 5G – hyper-connected, secure and experiential on an unimaginable scale.
What makes 5G different?
So far, with technologies like 4G, we have mostly imagined connectivity as human-to-human, or human to the internet. But, with 5G, that will no longer be enough.
The next natural evolution of connectivity is to not only connect everyday machines and devices to humans but machines to other machines. In fact, the entire promise behind 5G lies in connecting our entire environment with each other! With the number of connected devices globally set to triple by 2030 to 25.4 billion, terms like Internet of Things (IoT), Virtual Reality (VR), and Artificial Intelligence will no longer be just fanciful connotations of what will happen in the future. All these amazing experiences will be unlocked on the back of 5G.
According to 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), 5G delivers value by enhancing three major applications
Applications of 5G
What are the differences between the previous generations of mobile networks and 5G?
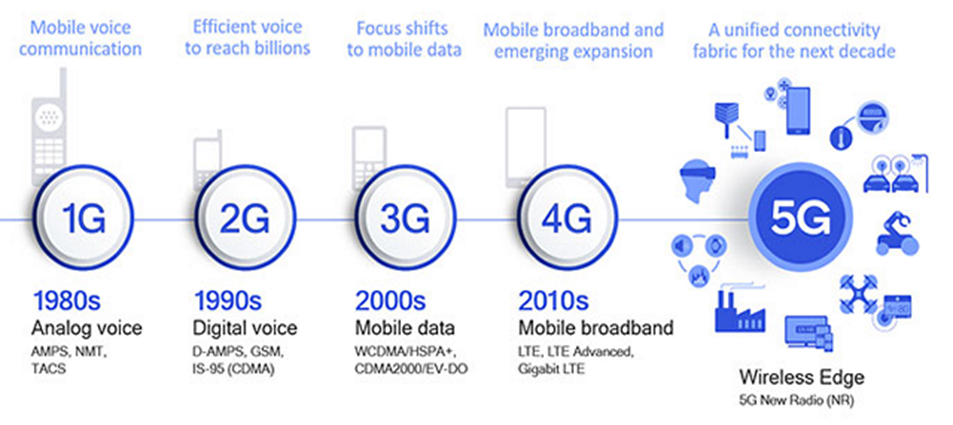
A: The previous generations of mobile networks are 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G.
First generation – 1G
1980s: 1G delivered analog voice.
Second generation – 2G
Early 1990s: 2G introduced digital voice (e.g. CDMA- Code Division Multiple Access).
Third generation – 3G
Early 2000s: 3G brought mobile data (e.g. CDMA2000).
Fourth generation – 4G LTE
2010s: 4G LTE ushered in the era of mobile broadband.
1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G all led to 5G, which is designed to provide more connectivity than was ever available before.
5G is a unified, more capable air interface. It has been designed with an extended capacity to enable next-generation user experiences, empower new deployment models and deliver new services.
With high speeds, superior reliability and negligible latency, 5G will expand the mobile ecosystem into new realms. 5G will impact every industry, making safer transportation, remote healthcare, precision agriculture, digitized logistics — and more — a reality.
The Impact of 5G Across Industries
The deployment of 5G is set to catalyse innovation across various sectors, revolutionizing industries and driving economic growth. Here are just a few areas poised to benefit from the advent of 5G:
Challenges and Future Outlook
While 5G holds immense promise, its deployment is not without challenges. These include the need for significant infrastructure upgrades, spectrum allocation issues, and concerns about security and privacy. However, as technology continues to evolve, these challenges are being addressed, paving the way for a future where 5G is ubiquitous, powering a new era of connectivity and innovation.
References:
